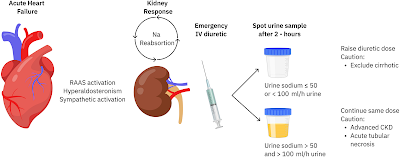
A recent editorial in JAHA discusses the use of urinary sodium (UNa) as a biomarker for monitoring and guiding diuretic therapy in patients with acute heart failure (AHF). Activation of the renin-angiotensin system in heart failure leads to sodium retention, hyperaldosteronism, and increased sympathetic activity, contributing to fluid overload. The authors highlight that assessing diuretic response through traditional methods, such as weight loss and urine volume output, can be inaccurate and logistically challenging. Instead, they propose using UNa measurements from spot urine samples taken 2 hours after diuretic administration as a more dynamic and early indicator of diuretic response.
The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines recommend using spot UNa analysis to evaluate diuretic treatment response in AHF patients. A low UNa (<50-70 mEq/L) at 2 hours post-diuretic administration is associated with inadequate diuretic response and suggests the need for more intensive diuretic therapy. The paper discusses observational studies and expert opinions that support this approach. However, it also points out limitations, such as the influence of kidney function, concurrent conditions like chronic kidney disease (CKD) and cirrhosis, and the potential loss of UNa's predictive strength after the first day of treatment due to changes in sodium excretion patterns.
The authors present data from studies that endorse the feasibility and efficacy of UNa-guided diuretic therapy in AHF. They discuss the ENACT HF trial, which showed improved natriuresis, diuresis, and shorter hospitalization duration with UNa-guided diuretic treatment. Another ongoing study, PUSH-AHF, aims to provide more definitive results on natriuresis-guided therapy using a stepwise diuretic approach.
The authors acknowledge that UNa assessment alone may not fully capture diuretic response and recommend combining UNa measurements with other indicators of decongestion, such as urine output. They also emphasize the importance of accounting for different patient factors like fluid overload status, kidney function, and the type of diuretics used.
In conclusion, while UNa-guided diuretic therapy appears promising for AHF management.. interesting and simple to do.
Love this figure from the paper

No comments:
Post a Comment